source: https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum-ii
C/C++ Solution to LeetCode problem 113. Path Sum II.
Problem
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return all root-to-leaf paths where the sum of the node values in the path equals targetSum. Each path should be returned as a list of the node values, not node references.
A root-to-leaf path is a path starting from the root and ending at any leaf node. A leaf is a node with no children.
Examples
Example 1:
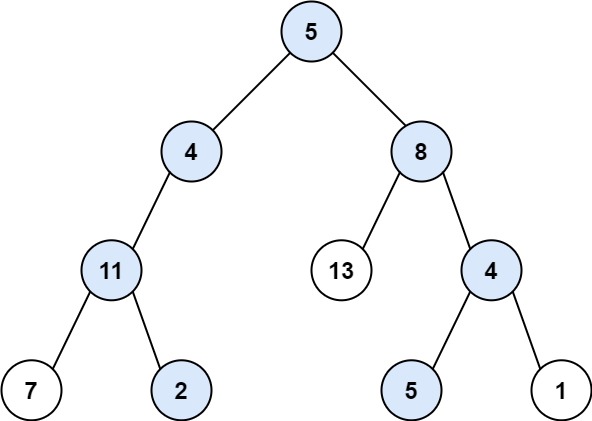
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
Output: [[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
Explanation: There are two paths whose sum equals targetSum:
5 + 4 + 11 + 2 = 22
5 + 8 + 4 + 5 = 22
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
Output: []
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
Solution
We will use recursion to perform a DFS (Depth First Search), at every node we will keep the sum (previous node’ values plus current node). Once the node doesn’t have children (left and right) it means we are at the end (leaf), and if the sum is equal to the target, then we have found a path.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> result;
void exploreNode(TreeNode* node, vector<int> path, int sum, int *target) {
if (!node)
return;
path.push_back(node->val);
if (!node->left && !node->right) {
if (sum + node->val == *target)
result.push_back(path);
return;
}
exploreNode(node->left, path, sum + node->val, target);
exploreNode(node->right, path, sum + node->val, target);
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
exploreNode(root, {}, 0, &targetSum);
return result;
}
};