source: https://leetcode.com/problems/rotate-list/
C/C++ Solution to LeetCode problem 61. Rotate List.
Problem
Given the head of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places.
Examples
Example 1:
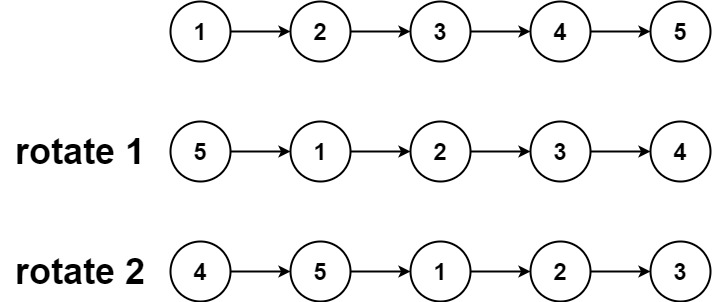
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
Output: [4,5,1,2,3]
Example 2:
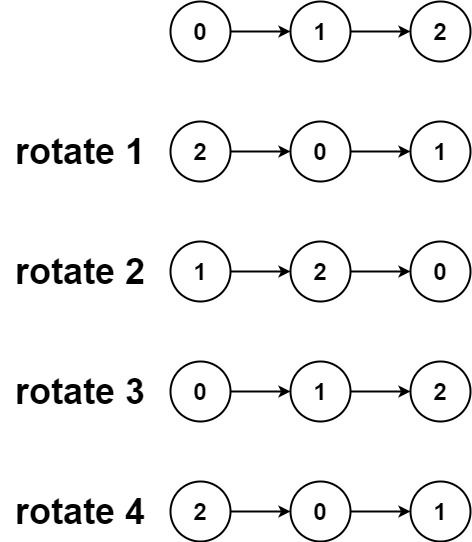
Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4
Output: [2,0,1]
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 500]. -100 <= Node.val <= 1000 <= k <= 2 * 109
Solution
For this, we use a similar approach to the one for problem 19.
- We move a
frontpointerktimes, and at the same time we count how many nodes we have. - If the pointer arrives to the end before movin
ktimes:- We can calculate how many times the pointer would be rotating through the list before moving
ktimes. - With this value, it wont be necesary to move the
frontpointerktimes, we only need to move itn = total_nodes % k.
- We can calculate how many times the pointer would be rotating through the list before moving
- Once the front node is at its final position, we start a
rearpointer at thehead. - From now, we move
frontandrearpointers together till thefrontpointer reaches the end. - Exchange pointers. the
front->nextwill point to thehead. - The new
headbecomeshead = rear->next. - Finally
rear->nextbecomes the end of the list so, it will point tonullptr.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode *f = head;
ListNode *r = head;
int n=0;
while (n<k && f->next != nullptr) {
f = f->next;
n++;
}
if (n <= k) {
f = head;
n = k % (n+1);
if (n==0)
return head;
while (n>0) {
f = f->next;
n--;
}
}
while (f->next != nullptr) {
r = r->next;
f = f->next;
}
f->next = head;
head = r->next;
r->next = nullptr;
return head;
}
};